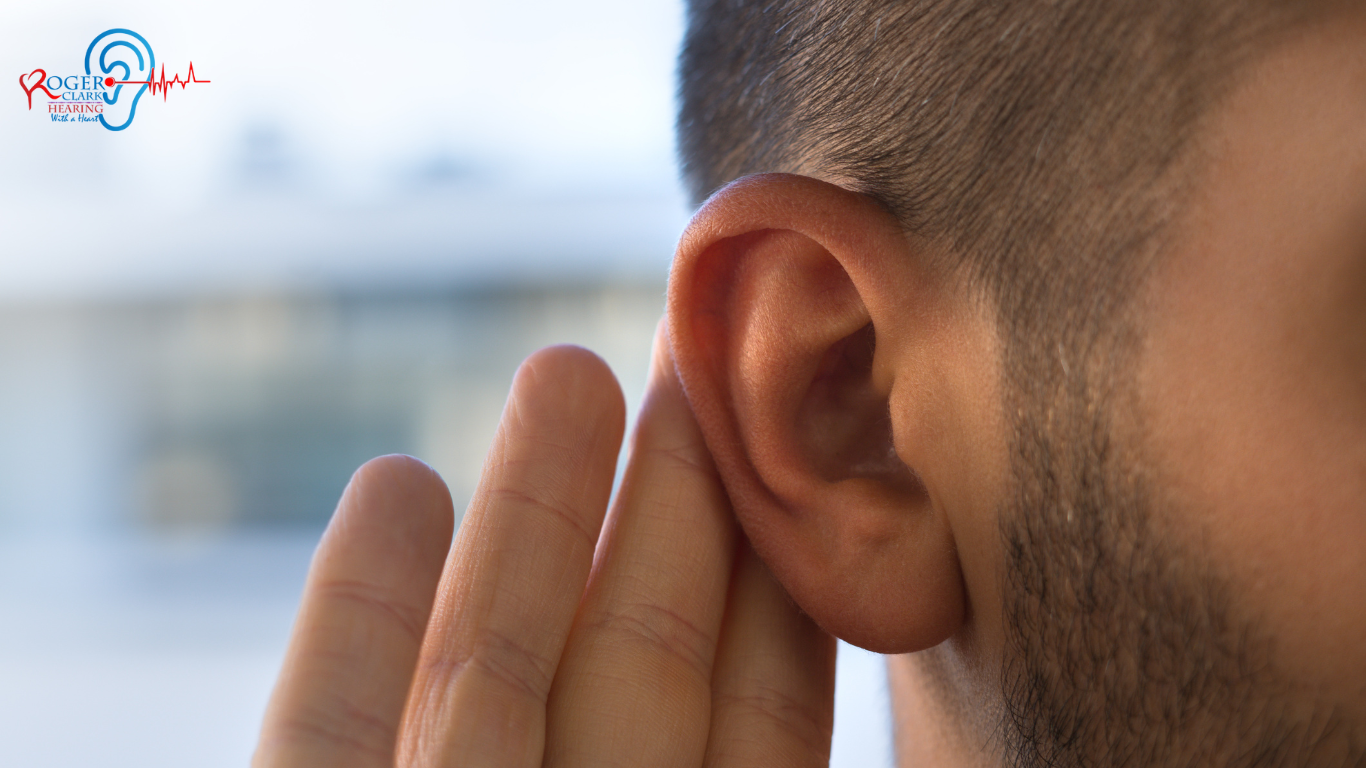
The human ear works in a highly complex way. Various mechanisms go on inside our ears, enabling us to hear different types of sounds.
So, if anything goes wrong with your hearing, you tend to become sad and depressed. It also makes it difficult for you to comprehend what people are saying. This prevents you from participating in social events and gradually dissolves you from society.
So, what are the different types of hearing loss? The two common types of hearing loss are sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss. Simply put, sensorineural results from damage to your inner ear, and conductive hearing loss results from damage to the middle or outer ear. Therefore, this blog will discuss these two types of hearing loss and their symptoms. Continue reading to find out more.
What is sensorineural hearing loss?
Sensorineural hearing loss, or SNHL, is a very common type of hearing loss experienced by people. As mentioned above, it comes from damage to the inner ear. It may also result from damage to the auditory nerve that transfers all the sounds you hear to your brain. When you experience sensorineural hearing loss, you may still be able to listen to some sounds but may find it difficult to comprehend certain sounds.
Sensorineural hearing loss can develop silently and go undetected for a long time. Therefore, it is essential to learn about the symptoms so that you can detect them as soon as possible.
What are the symptoms of sensorineural hearing loss?
- Trouble with hearing certain sounds like F OR S
- Having a tough time hearing high-pitched noises
- Decreasing the ability to listen to someone when they are talking
- Experiencing tinnitus in the ear (ringing, buzzing or roaring)
- Difficulty hearing anyone in noisy spaces
What causes sensorineural hearing loss?
Sensorineural hearing loss happens when the inner ear or auditory nerve is damaged for any reason. Most of the time, it happens because of damage to your ear’s tiny hair cells.
Aging
Your body finds it difficult to keep its cells healthy as you age. This is why ears often lose their function.
Loud noises
Hearing very loud noises can damage your inner ear. This condition is known as noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL). Depending on the sound you hear, it can occur suddenly or gradually over a period of time. If it were deafening, the damage would be quicker.
Ototoxicity
Ototoxicity refers to hearing loss caused by medication. This means that certain medicines damage your inner ear as and when you take them.
Tumors
Any abnormal growth in the ear can pressure the tiny hair cells in the ear drum and inner ear. When these cells cannot move freely, hearing can be affected. This can happen with both cancerous and benign tumors.
Trauma to the head
Any kind of blunt trauma to the head can damage your inner ear
Diseases
Autoimmune diseases like Lyme disease, Rheumatoid arthritis, Lupus, and Fibromyalgia can cause the inner ear to grow in size. They can also obstruct blood flow and damage the inner ear. One disease, Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease, or AIED, is specifically known for attacking the inner ear.
Infections
Infections like mumps, measles, and meningitis can cause temporary or permanent hearing damage. Such infections also include congenital cytomegalovirus.
What is conductive hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss, or CHL, happens when sounds fail to reach your inner ear. This makes it difficult for you to hear any sound around you. When this happens, something in the middle of the outer ear is blocking sounds from reaching the inner ear. If you experience conductive hearing loss, you may find type of hearing aids soft sounds and even noisy conversations complex.
What are the symptoms of conductive hearing loss?
The symptoms of CHL can vary according to the severity and the cause. Some people with conductive hearing loss also experience pain along with hearing loss. Following are a few symptoms of conductive hearing loss.
- Dizziness
- Buzzing, ringing or humming in the ears (Tinnitus)
- You may feel like your ears are plugged up
- Pain in one ear or both ears
- Difficulty hearing anybody talking
- Your voice may sound different to you
- Ears might feel like they are being pressurized
What are the causes of conductive hearing loss?
As mentioned above, anything that blocks your middle or outer ear can lead to CHL. The causes of conductive hearing loss are discussed below:
- Tumors (benign)
- Foreign things in the ear
- Too much earwax
- Inflammation
Also Read: Sensorineural vs. Conductive Hearing Loss: Understanding the Key Differences
Conclusion
This was all about sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. Thankfully, help is at hand for both cases. Contact us at Roger Clark Hearing for the best hearing aids in Waco.